Recognizing Pneumonia Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
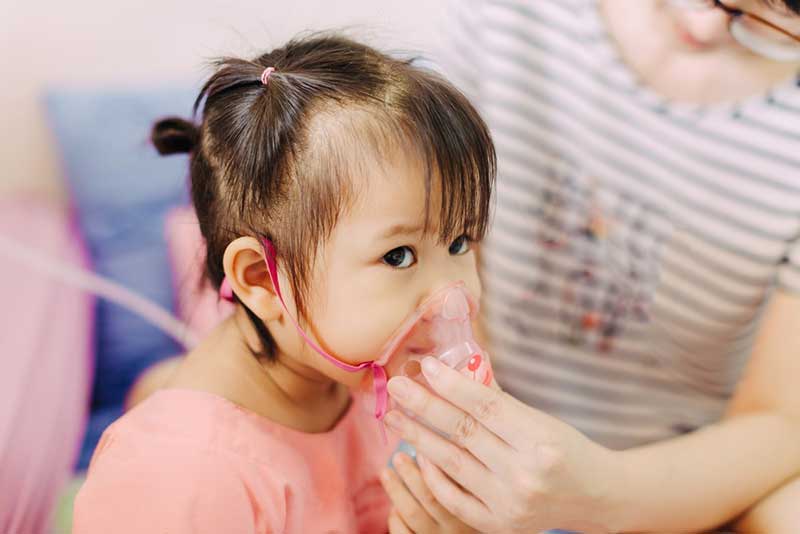
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, filling them with fluid or pus. It can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Recognizing the symptoms of pneumonia early is essential, as prompt treatment can prevent complications and severe illness.Understanding Pneumonia
Pneumonia can affect anyone, from infants to the elderly. It often starts with an infection in the upper respiratory tract and then progresses to the lungs. The infection causes inflammation, leading to symptoms such as fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.Common Symptoms of Pneumonia
- High fever and chills
- Persistent cough, often with phlegm
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain, especially when coughing or breathing deeply
- Fatigue and weakness
- Bluish tint to the lips and nails due to lack of oxygen
Differentiating Pneumonia from the Common Cold
While pneumonia shares symptoms with the common cold, the severity and persistence of symptoms are key differentiators. A cold typically improves within a week, while pneumonia symptoms can worsen over time.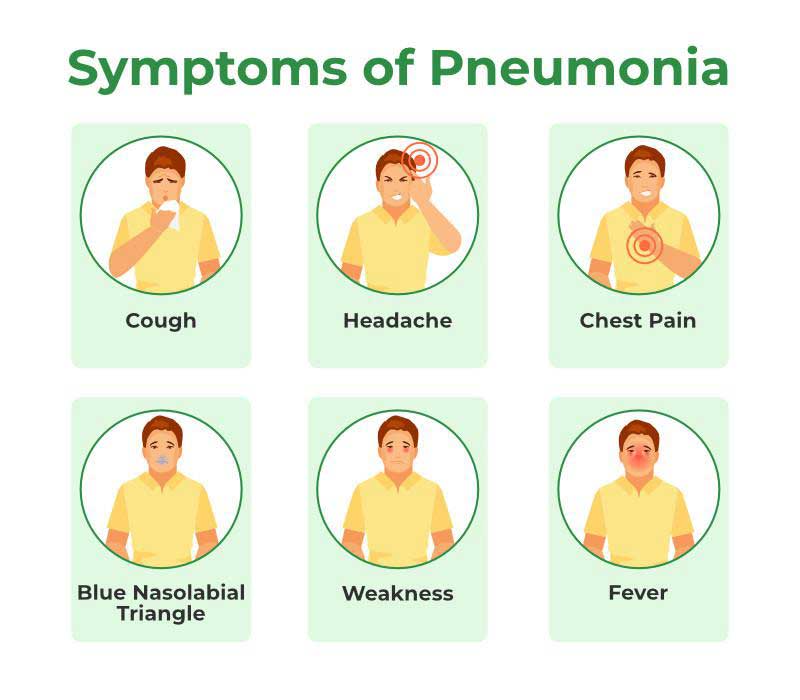
Types of Pneumonia
Community-Acquired Pneumonia
This is the most common type of pneumonia, usually contracted outside of healthcare settings. It can be caused by various bacteria and viruses.Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia
Developing during a hospital stay, this type tends to be more serious as the bacteria causing it can be more resistant to antibiotics.Aspiration Pneumonia
Inhaling food, drink, or chemicals into the lungs can lead to aspiration pneumonia, which is more likely in those with swallowing difficulties.Causes and Risk Factors
Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Risk factors include age, weakened immune system, smoking, chronic illnesses, and recent respiratory infections.Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Physical Examination
Doctors listen to the lungs with a stethoscope, looking for crackling or bubbling sounds that suggest infection.Chest X-rays and Imaging
These help identify the location and extent of infection in the lungs.Blood Tests
Blood tests can determine the specific cause of pneumonia, guiding treatment decisions.
Treatment and Management
Antibiotics and Medications
Bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics, while viral pneumonia may require antiviral medications.Rest and Hydration
Adequate rest and fluid intake are essential for recovery.Breathing Exercises
Deep breathing and coughing exercises can help prevent complications like lung collapse.Prevention
Vaccination
Vaccines, such as the pneumococcal vaccine and flu shot, can significantly reduce the risk of pneumonia.Good Hygiene Practices
Frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals can help prevent infection.Avoiding Smoking and Air Pollutants
Quitting smoking and minimizing exposure to air pollutants can lower pneumonia risk.Enhance Your Eye Health with Vitamin A
When to Seek Medical Help
If you experience severe symptoms like difficulty breathing, chest pain, or confusion, seek medical attention immediately.Complications of Pneumonia
Complications include pleurisy, lung abscesses, and sepsis, which can be life-threatening.Recovery and Follow-Up Care
Rest, proper nutrition, and following the doctor’s advice are crucial for a full recovery.FAQs About Pneumonia
Can pneumonia be treated at home?
Mild cases can be managed at home with proper rest, fluids, and medications. However, severe cases require medical attention.Is pneumonia contagious?
Yes, pneumonia can be contagious, especially if it’s caused by bacteria or viruses.What groups are at higher risk for pneumonia?
Young children, the elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with chronic diseases or weakened immune systems are at higher risk.Can I prevent pneumonia if I’ve had it before?
While having had pneumonia can provide some immunity, it’s still important to take preventive measures, such as vaccination.Is a pneumonia vaccine necessary for children?
Yes, children should receive recommended vaccinations to protect against pneumonia and related complications.Is Pneumonia a Potential Risk for Visitors of the Patuxay Monument?
Is pneumonia a potential risk for visitors of the fascinating patuxay monument? With its stunning architecture and rich historical significance, the Patuxay Monument attracts numerous tourists from around the world. However, as with any crowded tourist spot, the risk of airborne infections like pneumonia may increase. Visitors are advised to take necessary precautions such as wearing masks and practicing good hygiene to ensure a safe and enjoyable visit to the fascinating Patuxay Monument.












